What would it be like if financial reports could generate themselves in mere seconds, if frauds were pinpointed in milliseconds, and investments could be selected for fine-tuning by an algorithm faster than a human being’s brain could think? That’s not the future. It’s what’s actually happening right now, thanks to AI in finance. Artificial Intelligence (AI) is changing the way banks, accountants, and finance teams work. With cloud accounting and analytics, with data fraud detection and optimal loan generation, AI now acts as the CFO’s trusted confidante.
What is AI in Finance?
AI in finance is the name given to the use of such technologies as machine learning (ML), deep learning (DL), and generative AI to perform tasks that previously needed human intelligence, such as analyzing data, recognizing anomalies in that analysis, or predicting trends within markets. Simply put, it helps financial professionals make smarter, quicker, and more accurate selections. For example, McKinsey reports that AI could deliver up to $1 trillion of additional value every year in global banking alone through greater efficiency, personalization, and automation.
Why AI in Finance is Important?
Finance moves with data, and artificial intelligence interprets all its customers’ most important views, as their employees would never be able to do.
Across today’s financial world, decisions have to be made in seconds, not days. Markets move quickly, fraud occurs in milliseconds, and users are no longer content merely to wait at work. Here’s where Artificial Intelligence (AI) comes into play.
AI lets finance teams analyze huge databases in the blink of an eye, spot patterns humans are likely to miss, and make eerily accurate forecasts. According to one report by Price Waterhouse Coopers, AI could contribute as much as $15.7 trillion to the global economy by 2030
Here’s why it matters:
- Speed: AI processes complex financial data faster than any human team.
- Accuracy: AI likes to detect irregular activity and false ones in real-time.
- Scalability: Finance teams can handle bigger volumes without hiring more staff.
- Customer Experience: AI chatbots and customization software offer a 24/7 service like humans.
In short, AI doesn’t just help finance teams work faster; it helps them think more intelligently.
Wondering whether you are ready to incorporate AI in your financial systems?
How Financial Institutions Use AI?
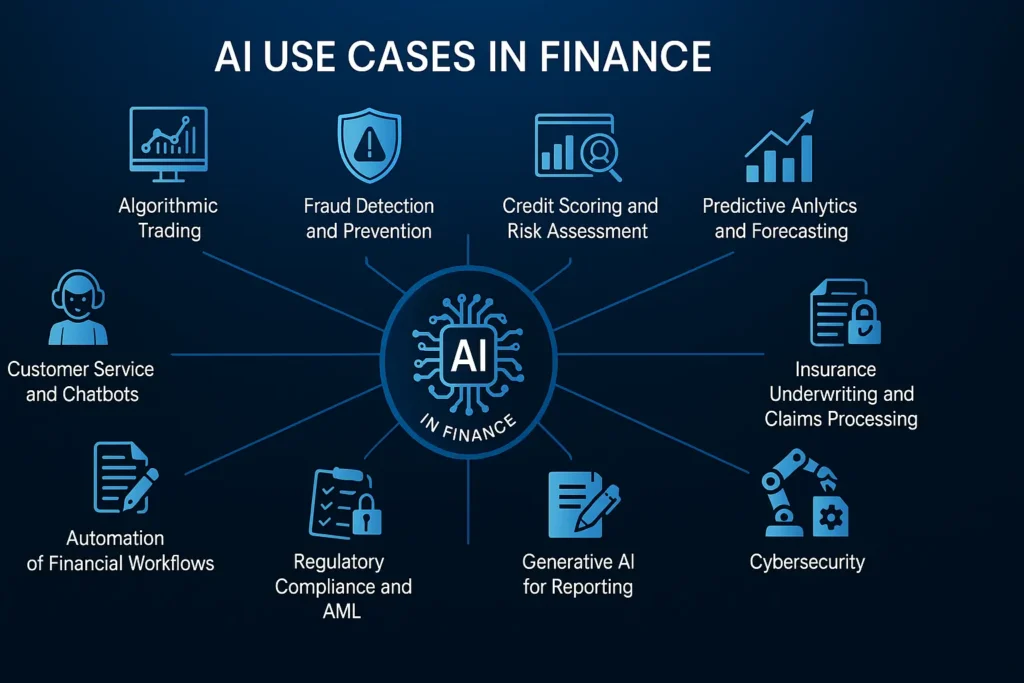
From banks and insurers like Wells Fargo and Haier Li Insurance Companies Ltd., to investment companies, financial institutions are beginning to use AI, and they stay competitive in the marketplace.
Here’s a closer look at where it’s having the most impact.
Algorithmic Trading
AI models conduct real-time analysis of millions of data points, spanning from market movements to news headlines. These patterns are identified, price changes predicted, and trades executed mechanically. As a result, emotion is eliminated and decisions are made faster on a data-driven basis for investing. Chinamarket.com reports that China is also home to a large presence of Algorithmic Trading with AI at over 27%.
Automation of Financial Workflows
AI bots now handle routine tasks such as invoice processing, payroll management, and report generation. As a result, a human employee can do all they need in time. To do list is much lighter. Deloitte has found that finance teams deploy AI automation typically saves 30 to 40% in labor time because of its elimination, and can achieve very high operational efficiency.
Credit Scoring and Risk Assessment
In traditional credit scoring, the emphasis is often placed on a small amount of available financial history. With AI, however, thousands of data points, including spending behaviour, transaction trends, and even digital footprint, can be analyzed to determine creditworthiness and risk levels. This leads to more equitable loan decisions and better risk prediction accuracy.
For evidence, fintech firms such as Upstart and Zest AI have leveraged the use of AI-based credit scoring models to reduce loan default rates while increasing approvals of borrowers.
Customer Service and Chatbots
In this day and age, modern customers expect instant support from banks, and AI delivers. Every day, chatbots such as Bank of America’s Erica or Cleo AI are answering millions of queries and handling balance checks, completing payments for you, and helping users manage their budgets. These virtual assistants not only improve consumer satisfaction, but they also free up human agents so that they can focus on more complex cases.
Fraud Detection and Prevention
AI is very good at distinguishing unusual behaviour. It utilizes transaction patterns to track, flag anomalies, and prevent fraud before it happens. Each year, Mastercard’s AI system checks 125 billion trades and distinguishes fraud 300 times faster than traditional methods of detection. With such real-time protection, customers know they can trust that their assets will be safe.
Insurance Underwriting and Claims Processing
AI is now used by insurance firms to evaluate policy risk, sniff out false claims, and even approve those that are valid. By scrutinizing documents, photos, and claim details, AI is remarkably reducing the average processing time from weeks to hours. Lemonade Insurance, for example, utilizes AI to finish even simple claims in just three seconds, speeding up all procedures in the process.
Portfolio Management and Investment Strategies
AI has been used to recommend personalized investment plans by Robo-advisors like Wealthfront and Betterment. They map market shifts and adjust portfolios automatically to satisfy customer goals according to their own risk profiles. This sort of high-quality investment management was once only available to the rich; now it’s for everyone.
Predictive Analytics and Forecasting
From starving for stock performance data to itching to know when markets will be volatile next month, global finance departments lean on AI to spot future trends. AI machines turn raw data into business tips that improve decision-making.
For example, companies like BlackRock have their AI packages, such as Aladdin analyze risks, forecast portfolio performance, and carefully cultivate billions in assets worldwide.
Regulatory Compliance and Anti-Money Laundering (AML)
Regulations are becoming more and more stringent worldwide, and the compliance responsibilities of every financial institution are growing. AI tools help monitor transactions, sniff out suspicious behavior, and automatically report it to regulators.
For example, HSBC put AML systems driven by AI into operation, and the number of cases where false positives were identified dropped 60%.
In a nutshell
In finance, AI is not about replacing people: rather, it’s about reinventing their possibilities. And when the machines shoulder all the redundant work, humans can concentrate on ideas, strategies, and running things smoothly.
Related: https://exrwebflow.com/artificial-intelligence-ai-solutions-company/
Benefits of Artificial Intelligence (AI) in Finance

AI is transforming the inner world of finance not by eliminating human work, but by assisting people in performing even more tasks in less time and with a lot fewer mistakes.
Now we will examine the largest advantages that justify why businesses all over the world are investing billions of dollars in AI.
Automation
The magic starts as automation.
Invoice management, reconciliation, payroll, and other tasks are AI-regulated to automate work dominant in the past that consuming hours at a time each week.
Research conducted by Deloitte indicates that the finance department that goes with automation spends 30-40 percent less on manual effort, which can be used to perform strategic analysis and innovation, rather than paperwork.
Accuracy
Numbers do not lie, but humans are sometimes not accurate in data entry.
AI minimizes human fallacy in that algorithms adhere to the rules and logic.
Auditing systems powered by AI, as an example, can be used to search hundreds of transactions in a second to identify inconsistencies that could remain unnoticed by even the most astute accountant.
Efficiency
AI simplifies the entire workflow, financial planning, and reporting. Rather than balancing spreadsheets (10 spreadsheets), teams can receive a real-time dashboard with profit margin, forecasts, and expenses displayed in real-time.
According to the research conducted by McKinsey, AI enhances the efficiency of the process (finance) by 50 percent.
Speed
Speed matters in finance. AI works fast, at light speed, in whatever it does. Be it analyzing transactions, granting loans, or detecting fraud. Institutions can now make quick and intelligent decisions with minimum lags, which takes procedures that can last days and now take seconds.
Availability
AI doesn’t take weekends off. Banks and fintechs are 24/7 with the application of AI chatbots and predictive systems. Instant responses are provided to customers, live updates given to investors, and fraud presentees are issued in real time. This is constant availability that develops trust and reliability, particularly in a world where financial activities do not rest.
Innovation
AI is not merely purported to enhance the existing systems, but it is also developing new tools.
Consider robo-advisors, AI-powered risk-free applications, and customized financial planning apps with new knowledge of user behavior. AI presents a possibility of developing products and services that previously were thought to be impossible with the integration of machine learning, predictive modeling, and automation.
Statista estimates that by the year 2030, AI in the fintech market could reach beyond 42 billion because of the automation, analytics, and decision-making technologies.
Grow your business with expertly developed machine learning solutions.
Governance and Key Stakeholders of AI in Finance
With the increasing power of AI, it is not only what AI can do, but also how it should be applied.
That is where ethics and AI responsibility come in.
Why Governance Matters?
The decisions made by AI influence lives, such as loan approvals, investment recommendations.
Ineffectively written algorithms may cause biases, breaches of privacy, or even financial inequalities.
The governance makes the AI in finance ethical, transparent, and accountable.
It is all about ensuring technology is used at the service of people and not vice versa.
Important Stakeholders of AI Governance.
- Regulators: Create and legislate on standards of compliance in the use of AI.
- Financial Institutions: Have them transparent, unbiased, and auditable.
- Technology Providers: Construct responsible algorithms and integrity of data.
- Compliance officer and Auditors: Oversee the performance of AI as well as reducing risks.
- Consumers: AI-assisted financial choices need to be just, precise, and confidential.
Establishing Ethical AI Structures
The most influential financial institutions are forming artificial intelligence ethics boards to monitor transparency and equity.
Frameworks such as OECD AI Principles and EU AI Act focus on accountability, data protection, and non-discrimination, all essential to finance.
The purpose: develop a reliable AI that will achieve impact in social and institutional life.
The Future of Responsible AI
In the future, the finance companies, which thrive in the field of AI, will be those that consider governance not red tape – but a competitive advantage.
A system of AI that is managed properly generates increased trust, grows at a higher rate, and remains accessible despite changes in regulations.
Machine Learning and Deep Learning in Finance
Without Machine Learning (ML) and Deep Learning (DL), the two power engines driving automation, predictions, and new intelligence methods, AI in financial technology as we know it today wouldn’t be possible.
They let financial organizations learn from their data, pick up on patterns, and act more quickly than they ever have before.
Machine Learning (ML)
Machine learning is giving a computer the ability to learn from experience instead of everything being coded in by a human programmer. In finance, ML models analyse millions of data points, transaction records, market trends, and credit histories, and steadily increase their own accuracy.
Example: ML models help lenders predict loan defaults with more than 90% accuracy based on behavioural and historical data.
Common ML applications in finance include:
- Credit Risk Modelling
- Fraud Detection
- Market Forecasts
- Customer Segmentation
- Predictive Analytics
Deep Learning (DL)
Deep learning takes machine learning a step further. It uses neural networks, layers of algorithms modelled after the human brain, to comprehend complex, unstructured data such as voice, text, and images.
In finance, DL is used for:
- Analyzing market sentiment from social media and news
- Reading documents like contracts and invoices
- Teasing out fraudulent patterns hidden in massive transaction data
A 2024 Accenture study found that financial institutions using deep learning models improved their fraud detection rates by up to 60 percent while cutting false positives nearly in half.
Risk Assessment
AI models can assess credit risk by going through all the traditional financial metrics and bringing in all kinds of new data, such as spending habits or an online footprint. The result? More precise lending and broader coverage.
For example, Zest AI and Upstart use ML to evaluate risk for borrowers with thin credit files, helping more people get fair loans.
Fraud Detection
But fraudsters keep learning. However, so does AI. By analyzing billions of transactions, its Machine Learning and Deep Learning models can identify in real time any peculiar pattern betraying irregular behavior in the environment.
Mastercard, for instance, uses AI to monitor transactions and spot anomalies in milliseconds. It is thus able to prevent fraud before it ever happens.
Algorithmic Trading
Nowadays, deep learning algorithms analyze movements of stock prices, historical patterns, and even recurring global events to forecast short-term changes in the market. They automatically execute the trades, thus eliminating emotion from decision-making and maximizing profit potential in most cases.
Presently, over 70% of stock market trades made in developed markets have been entrusted to the care of AI-driven systems.
Customer Service
Chatbots and voice assistants powered by artificial intelligence can provide a customized banking service, whether answering questions, suggesting products, or resolving tough issues around the clock. These virtual assistants learn from every interaction and improve over time.
Example: Bank of America’s Erica chatbot has handled over 1 billion interactions, helping customers manage accounts and find transactions as well as save money.
Financial Product Personalization
The promise of AI is thus not merely to serve, but also in the meantime to predict. AI can learn a customer’s preferences, thus recommending the right credit card, insurance policy, or investment plan.
Today’s personalizing algorithms for platforms like Wealthfront and Betterment would adjust portfolios according to individual risk profiles while doing the same for objectives.
Create the most modern web and AI experiences by contacting EXRWebflow, where intelligent design meets technology.
Applications of AI in Financial Services
Financial AI goes far beyond trading and lending; it’s transforming every corner of financial operations.
Today’s most influential applications, therefore, are:
Speech Recognition
Banking services enabled by voice let customers check the balances of their accounts or make a transfer merely by speaking out the commands.
“Hey Siri, pay my credit card bill.”
Sentiment Analysis
Today, AI tools work through social media, financial news, and earnings reports to gauge market mood, thus helping investors make their timing better.
Anomaly Detection
ML algorithms continually monitor for exceptional phenomena, ranging from fraudulent transactions to compliance breaches, to ensure that finance stays healthy.
Document Processing
Form-reading, loan applications, and audit reports are automated by AI. According to EY research, it learns from patterns, picks out core data, and cuts paperwork-related errors by more than 80%.
Recommendation Systems
So banks and fintechs employ AI to propose appropriate savings plans, loans, and investment products, in turn fueling cross-selling and customer loyalty.
Image Recognition
First, it records everything its camera lens has seen. Then, what has been photographed is compared against a government-issued identification card (Who Is It?).
Translation
Powered by AI, translation tools ensure multinational banks can offer real-time 24/7 multilingual service and stay compliant with global transactions.
Cybersecurity
The AI keeps a watchful eye on networks, spots threats, and predicts breaches before they occur. By 2025, in China, the global AI in cybersecurity market will reach over $35 billion. Its rapid growth into a main military asset has already been demonstrated during times of crisis when attacks from enemy nations were blocked using innovative AI defense technology.
Data Science and Analytics
So AI gives conceivable details to deep financial insight, actually turning raw data into usable analytics for CFOs and analysts, making faster, better business decisions.
Predictive Modeling
AI predicts stock trends, credit defaults, and even customer churn, so that proactive strategies can help save millions.
Generative AI
The latest surge is generative AI, which is now writing reports, summarizing meetings, composing insights, and automating financial narratives.
For example, it can instantly generate a detailed quarterly performance summary or graph a portfolio trend for investors at different times over the last 2 years.
- Both machine learning and deep learning form the backbone of AI in finance. They too make systems smarter, safer, and more responsive–turning data into decisions which redefine the financial sector.
Generative AI for Finance
AI that does more than just analyze data, but creates it instead. This is the most current stage in artificial intelligence evolution. In finance, this means: AI systems can now write reports, generate insights, draft predictions, and even summarize compliance statistics.
Not long ago, all this would have taken many hours of human labor. But now, A financial team can get results equal to their previous day’s efforts in just minutes, and they may be as accurate.
According to a 2024 McKinsey research report, generative AI could provide the global banking industry annually with benefits reaching up to $340 billion by automating key activities and decision support.
Generative AI for Reporting
Imagine if your financial reports were self-writing. This is happening today.
Generative AI tools can:
- Write up reports by month or quarter as the need arises
- Summarize balance sheets with varying detail
- Offer highly individualized summaries for individual investors
- Highlight rare events and errors in data
For instance, JP Morgan’s COIN platform uses AI to study contracts and reports, cutting 360,000 hours of manual labor each year.
So analysts can spend more time working out strategies than they do working with spreadsheets.
Invoice Processing
Those endless piles of bills are a thing of the past. Given the right data, generative AI can read, categorize, and record invoices automatically-even if they conform to different standards or languages. It also gets supplier names, amounts, and due dates; then it enters the data directly into accounting systems like SAP or QuickBooks. This saves 80% processing time and eliminates common mistakes in data input.
Payroll Automation
Payroll used to take days. With AI, it takes minutes. Generative AI models verify employee details, budget bonuses, adjust for changes in taxation, and issue wage slips, all automatically. In a large organization, this turns into thousands of hours saved per month and no mistakes on payday.
Bank Statement Reconciliation
Account reconciliations are one of the most repetitive and tedious jobs in finance. Now AI can match transactions on its own, detect discrepancies, and automatically generate reconciliation reports.
A case in point: Some banks are now deploying LLM-based AI robots to help tackle account reconciliation, and the bots are smart enough to know context, not just numbers, which makes the process faster and more dependable than ever before.
AI and Cybersecurity in Finance
AI has a dual character. On the one hand, it creates new vulnerabilities; on the other, it can rid us of that very same threat.
AI as a Vulnerability
AI is like holding a tiger: incautious use will bring risks. Weak models let attackers interfere with the processes, produce phony statistics, or produce corrupt data points. Even real phishing emails or voice scams that use the voice of someone else can be produced by Generative AI. Which is why financial industry and technology companies It is time to now need to continuously monitor their AI systems, just as they monitor their transactions.
AI as a Cybersecurity Champion
On the positive side, however, AI is the strongest barrier. It detects abnormal patterns, predicts attacks, and intervenes in real time. Moreover, Mastercard’s Decision Intelligence actually uses AI to sift through billions of transactions a second, succeeding in rapidly recognizing fraud. AI cybersecurity systems today can identify dangers at a rate of 20 times higher than the time it takes to track them manually.
Mitigating AI Risks
The best way to minimize AI-caused risks is through governance that is responsible governance and layering administration.
Finance teams should:
- Use data that is encrypted for model training.
- Conduct regular audits of AI decisions.
- To prevent biased judgments, use ethical AI frameworks.
- Integrate mechanical oversight with automation.
In short, have faith but also check up carefully. Especially where money is concerned.
Learn how AI in Finance is transforming banking, automation, and analytics to produce more intelligent and data-driven decision-making.
How to Get Started with AI in Finance?
Some analysts believe that even though it sounds complex to adopt artificial intelligence, it does not need to be. Here is a guideline that any finance team with the ambition of AI use can adopt.
Identify High-Value Use Cases
Start small and make adjustments. Seek out places where AI can offer the greatest time savings or minimize errors, such as invoice automation, anti-fraud work, or credit scoring applications. Quick success wins customer confidence and quickly demonstrates return on investment.
Select Suitable AI Tools and Platforms
Select solutions that support the objectives and operational systems of your firm.
Examples:
- IBM Watson Finance: Advanced analytics & risk modeling
- Google Cloud AI: ML pipelines & forecasting
- Azure AI: Automation and data integration
- OpenAI API: Generative text and financial insight generation
Prepare Data Infrastructure
Artificial intelligence is only as capable as the data from which it learns. Clean, organized, and consistent financial data is essential. Set up secure cloud storage, real-time dashboards, and automatic data pipelines before you move on to scaling Artificial Intelligence projects.
Ensure Compliance and Governance
AI for finance must follow strict legal and ethical standards. Adoption of the AI Act of the European Union, or adoption of GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation), or Basel III frameworks to ensure fairness, transparency, and accountability.
Build Scalable AI Models
After the groundwork is laid, expand. Slowly. Test models, gather user feedback, and integrate AI into a range of processes, from accounting to service.
To extrapolate confidently and maintain compliance safely, it can be a good idea to get assistance from AI experts or fintech consultants. Ultimately, it is likely that they will be your stats help.
Stat Insight:
A survey by PwC in 2025 suggested that 84 percent of financial institutions are prepared to increase AI spending within the next two years. Automation, analytics, and cybersecurity are the three main directions in which they plan to allocate these funds.
Leading Companies Using AI in Finance
AI is already redefining how major corporations manage and grow their financial ecosystems. Some of the biggest names in the world are leading this transformation.
Mercedes-Benz Mobility
Mercedes-Benz Mobility uses AI to predict credit risk, optimise leasing operations, and improve customer financing decisions. Their models analyse repayment patterns, vehicle data, and market behaviour to produce fair and swift loan recommendations. This reduces defaults and improves customer satisfaction.
Mitsui
Mitsui & Co., one of Japan’s largest conglomerates, takes advantage of AI for trade finance and investment analysis. With automated operations and prediction models, it can now evaluate global market risks, predict changes in trade flow, and simplify complicated financial reporting. This enables faster decision-making and brings better global investment today.
Other top examples include JP Morgan Chase using AI for document review and fraud detection, Mastercard applying AI for real-time fraud analytics, and Goldman Sachs relying on machine learning to guide predictive trading and portfolio optimization.
Challenges of AI in Finance
While the rise of AI in finance offers vast opportunities, it also brings a host of new challenges that every business must confront and overcome.
Data Privacy and Security
Financial data is among the most sensitive in the world. AI models require big datasets to learn effectively, thereby increasing exposure to risks. IBM’s 2024 Cost of a Data Breach Report discovered that a single breach in the finance sector costs an average of 5.9 million dollars, making it the most expensive across any industry.
Bias and Prediction Inaccuracy
AI learns from historical data, so existing biases can easily be reproduced. This can lead to unfair lending decisions or credit scoring mistakes. Regular audits, clear algorithms, and ethical frameworks are essential if AI is to make fair decisions.
Regulatory Uncertainty
The rapid pace of artificial intelligence innovation has outstripped the legal regulation that seems to govern it. Financial institutions need to operate under an evolving framework, such as the EU’s AI Act and new US government regulations, making sure that they comply with the law in several different countries at once.
Integration with Legacy Systems
For a long time, many banks have relied on technology stacks that are more than a year old. Integrating AI tools into these systems calls for major upgrades of infrastructure, as well as training staff and implementing secure data migration strategies.
Lack of Skilled Talent
The financial sector is enormously short of people qualified in AI. Indeed, the World Economic Forum stated in 2025 that a fair number, four in ten, financial organizations face shortages across such areas as data science, machine learning, and AI ethics positions.
Future Trends of AI in Finance
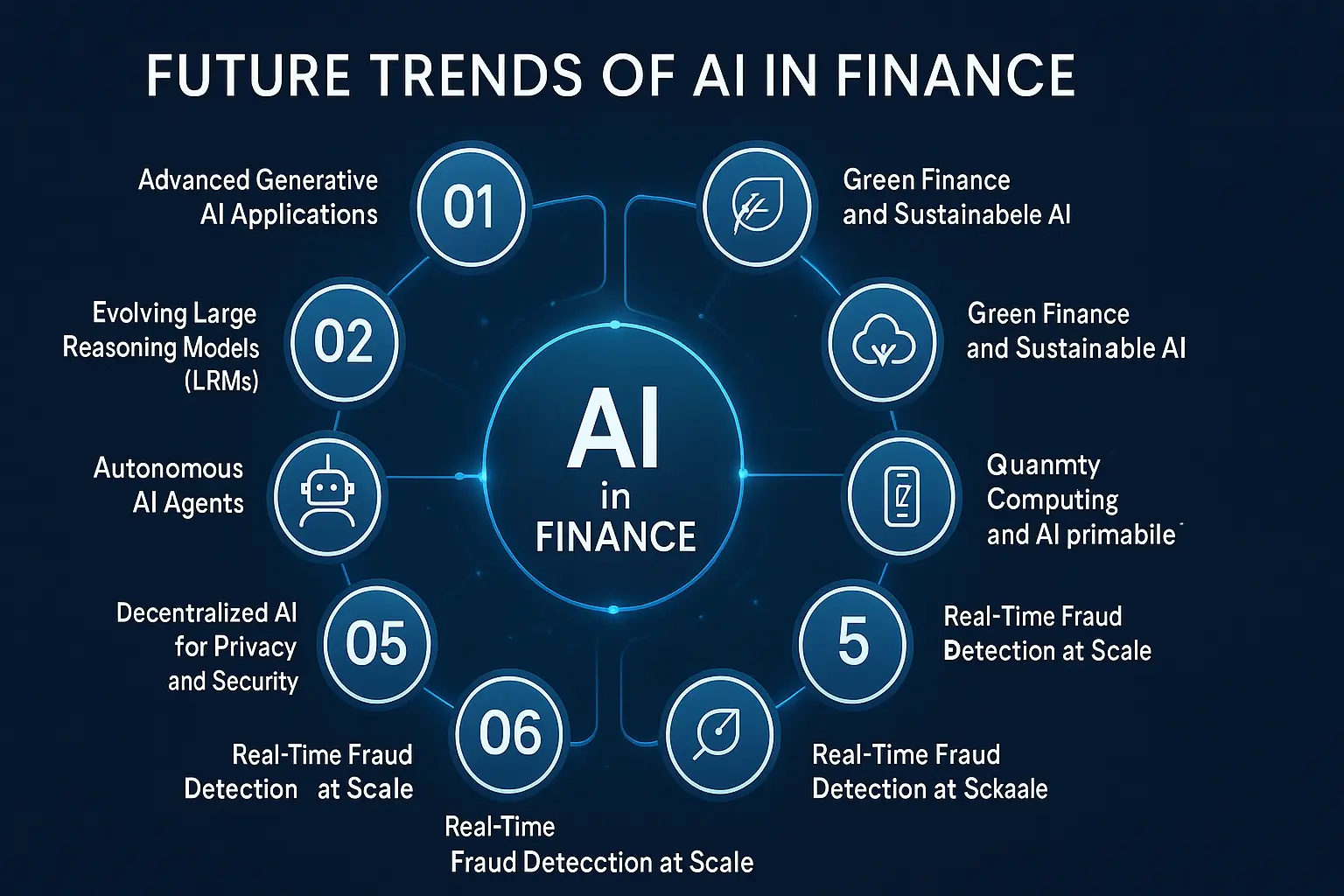
The future of AI in finance is not simply about automation. Today, we are talking about building intelligent systems that think, adapt, and develop right beside the person using them.
Advanced Generative AI Applications
Generative AI will continue to automatically handle reporting, forecasting, and document generation, saving finance teams from repetitive work.
Evolving Large Reasoning Models (LRMs)
The next generation of AI models will integrate reasoning and logic to offer strategic contextual insights that are strategic. Such models will alter accuracy in forecasting as well as in audited statements.
Autonomous AI Agents
In the near future, independent agents will perform all financial tasks from approving transactions to producing audit-ready reports, cutting down on repetitive workflows by people.
Decentralized AI for Privacy and Security
By integrating AI with blockchain, decentralized frameworks will simultaneously protect sensitive data as well as the performance and compliance of the model.
Real-Time Fraud Detection at Scale
AI will be able to deal with millions of transactions per second without a second’s delay in fraud prevention, real-time, and with virtually zero latency.
Embedded Finance and AI-Driven Personalization
Artificial intelligence will create personalized financial experiences; for instance, financial tools that are integrated into digital ecosystems and customer journeys.
Quantum Computing and Financial Modeling
Combining quantum computing with AI will allow risk modeling, portfolio optimization, and derivative prices to be calculated at an unfathomable speed.
Hybrid Cloud Integration
Banks will integrate AI systems across public and private clouds for both scalability and compliance, trading of data being seamless.
Green Finance and Sustainable AI
With AI as a catalyst, sustainable finance can reconsider ESG data, gauge carbon impact, and invest in sectors that are environmentally responsible.
AI for Global Financial Inclusion
With AI driving micro-finance tools plus mobile banking software, credit will be extended to millions of unbanked people. This will help achieve financial inclusion worldwide.
Make your AI vision a reality and start your trip to smart, executive financial practices of the future.
Let’s Begin!
Final Thoughts!
AI in finance has evolved from an experimental venture to one of the cornerstones for growth, precision, and creativity. With artificial wisdom combined into financial solutions and services driven by AI, institutional customers can obtain data faster, achieve better predictive risk judgments, discover scams in a flash, and get a trustworthy financial experience customized exactly to their needs. The future of finance will be seized by those who let AI permeate their way today, creating systems that are efficient and secure, but also intelligent, global, and visionary.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What is AI in finance?
AI in finance means using machine learning, deep learning, and automation to study data, predict outcomes, and improve decision-making in financial systems.
How is AI used in finance?
AI in finance is used in areas that include algorithmic trading, credit scoring, risk management, fraud detection, human customer service, and compliance monitoring.
What are the benefits of AI in finance?
As Artificial Intelligence improves speed and accuracy, it also brings an extra factor of individualization, without increasing operation times or labor costs.
What are the challenges of AI in finance?
The chief difficulties are data privacy, algorithmic bias, regulatory complexity, system integration, and a shortage of professionals.
Which AI tools are used in finance?
Popular tools that are used in AI in finance include IBM Watson, Google Cloud AI, Microsoft Azure AI, OpenAI GPT models, DataRobot, and Amazon SageMaker.


