Have you ever asked yourself what an AI agent is and why all big technology firms are discussing them? It may be confusing, such as in cases where the terms used in AI overlap. Chatbots, assistants, LLM, and now agents. What is different? What actually matters?
Here is the simple truth.
The majority of users believe that AI agents are smarter chatbots. However, that conviction makes them fail to see the actual prospect. Something much more valuable is done by an AI agent. It knows what to achieve, prepares a scheme, acts with the help of tools, evaluates its outcome, and gets to know its errors. It acts more like a digital employee rather than a digital helper.
And this shift is big.
According to Gartner, in the coming years (as soon as 2028), over 70 percent of enterprise apps will feature agentic AI. It will imply that the method of automation of work of companies, the ways of decision-making, are going to be altered rapidly.
This guide breaks it down in the most simplistic manner possible. If you wish to know how these agents work, why it is important, and how they are already remaking the business processes of industries.
What is an AI Agent?
An AI agent is defined as a system that is capable of comprehending an objective, making choices, and acting independently of that objective to accomplish it. It does not just respond to questions. It works, employs the tools, results, and experiences, and assesses them.
To define what an AI agent is in a basic way, we should consider it a digital worker and not a simple chatbot. It can figure out what you desire, what steps are appropriate, execute the moves, and make adaptations, in case something changes.
There are three things that an AI agent handles very well.
- It observes information.
- It makes reasoning about what the information conveys.
- It acts to achieve a goal.
This blend of comprehension, strategizing, and execution is what provides the agents with a space over and above mere automation. They can perform multi-step activities, revise when situations change, and get better at what happens. Due to this, companies use AI agents to automate their processes, assist customers, process data, compose informational reports, and handle the software systems on their behalf.
Book a 30-Minute Strategy Call today and discover the potential of the AI agents in the business.
Key Characteristics of AI Agents

There is a combination of properties that enable the AI agents to stand on their own feet, making decisions and enhancing themselves with time. All these features make a standard AI model a system that can be purposeful.
Autonomy
An artificial intelligence agent is able to work without supervision by humans. The steps are managed by the agent who determines the goal. It determines the way forward depending on the circumstances. This enables the agent to be able to execute long or complex tasks independently.
Goal-oriented behavior
Agents do not act randomly. They are geared towards a sense of clarity. After setting a goal, the agent will divide it into tasks and select the actions that will favor the desired outcome. This renders the system driven.
Perception
The agents collect data in the surroundings. This can be either text or data, or user input or software indication. Perception enables the agent to interpret what is going on and make some real-time adjustments to its decisions.
Rationality
Activities and goals are matched to the action chosen by an agent. It is a comparative action that analyzes options and makes predictions and decisions on the most successful courses of action. This is a logical method of assisting the agent in arriving at decisions that seem rational and consistent.
Proactivity
Instructions are not waited for by agents. They take initiative. The agent will be the first to move in case there is something to be done to achieve the goal. Automation that is proactive and not reactive is central to this feeling of intelligent automation.
Continuous learning
Agents become better with experience. They review the outcomes of their behavior and revise their future behavior. This helps them to be more precise, efficient, and more in line with user expectations over time, through this learning loop.
Adaptability
The agents are adapting to a change in conditions. They change their plan in case of the appearance of new information. In case of the failure of one step, they resort to another one. Flexibility enables agents to operate in changing conditions without reduction.
Collaboration
The agents are able to interact with human beings or other agents. They divide and conquer, share and organize actions. This is a collaborative skill that assists multi-agent systems in which numerous agents collaborate on sophisticated workflows.
AI Agents vs. Other AI Systems
The way AI agents are distinguished among other AI systems can shed light on the need to comprehensively understand why such agents are important and when to apply them.
AI agents vs LLMs
An elaborate language model is a logic machine. It forecasts text, answers questions, and patterns.
An AI agent is a complete system that is constructed on top of an LLM. It incorporates planning, memory, goals, tools, and the capability to act.
The LLM is the brain. The agent is the worker.
AI agents vs chatbots
A chatbot is a type of robot that answers:
- An AI agent responds and acts.
- Chatbots contain information.
- Agents achieve outcomes.
This is the major difference. One gives answers. The other completes tasks.
Agentic vs non-agentic chatbots
- The non-agentic chatbots remain in dialogue. Their ability to do multi-step tasks is lacking.
- The agentic chatbots can organize, employ tools, as well as perform workflows.
This is because this transformation transforms a chatbot into a task-performer rather than a support tool.
AI agents vs AI assistants
- AI assistants are synchronous yet rely heavily on user input. They wait for instructions.
- AI agents strive to achieve a purpose and do not require attention to accomplish it.
Assistants support. Agents operate.
Reasoning models vs agentic systems
The model of thinking is enhanced by reasoning models such as OpenAI o3 or DeepSeek R1. They improve reasoning, strategizing, and decision-making.
It is not sufficient to reason.
The agentic systems involve the combination of reasoning, memory, goals, tools, and action.
In simple words:
Better reasoning takes place in a reasoning model.
That thinking is acted upon by an agent.
Suggested Read: https://exrwebflow.com/ai-avatar-services-for-e-learning-content-creation/
How Do AI Agents Work?
The agents of AI obey a straightforward procedure. They watch what is occurring, reflect upon what is occurring, and take some action to achieve an end. This process is repeated until completion of the task. The ability of agents to have a combination of reasoning, planning, memory, and the use of tools makes them work as digital workers rather than communication workers.
Core Components of AI Agent Architecture
Every AI agent is equipped with a system of elements that enable it to comprehend goals, devise actions, and take a significant step.
| Component | What It Does | Why It Matters |
| Foundation Model | Interprets instructions, reasons through problems, and generates decisions. | Works as the agent’s brain. Without it, the agent cannot think or understand language. |
| Planning Module | Breaks a goal into smaller steps and organizes them in the right order. | Allows the agent to handle multi-step tasks and stay goal-focused. |
| Memory Module | Stores past actions, context, data, and results for future reference. | Helps the agent stay consistent, avoid repeating mistakes, and work across long tasks. |
| Tool Integration | Connects the agent to software tools, APIs, browsers, and apps. | Gives the agent the power to act in the real world instead of only producing text. |
| Learning and Reflection | Evaluates actions, reviews outcomes, and updates future behavior. | Allows the agent to improve over time and become more accurate and reliable. |
AI Agent Workflows
AI agents do not act randomly. They enjoy an orderly work process that informs their observations, decisions, and actions.
Traditional sense–think–act loop
It is an early artificial intelligence model. The agent is sensitive to information. It ponders the meaning of the information. It is founded on that knowledge and thus operates on it. This is a continuous loop until the objective has been achieved.
Agentic chatbot workflow
In modern agents, there are some additional layers.
- They identify the user’s goal.
- They plan a sequence of tasks.
- They apply tools or an external system.
- They check the results.
- They think and make changes when necessary.
With this workflow, agents are able to control multi-step procedures in a precise manner.
AI Agent Reasoning Paradigms
Paradigms of reasoning assist agents in thinking better. They dictate the choice of the agent on the course of action.
ReAct
ReAct can be abbreviated to mean reasoning and action. The agent believes, acts, watches, and assimilates in miniature strides. This will enable it to learn throughout the process as opposed to doing all the planning in advance.
ReWOO
ReWOO is an abbreviation that means reasoning without observation. The agent composes a complete plan at first. It will merely accumulate information when and as it is needed by the plan. This method ensures less waste in terms of the utilization of the tools and renders the agent more productive.
Additional reasoning paradigms
Chain of thought reasoning, tree exploration, and graph planning constitute other techniques. These assistance agents deal with complicated decision-making, thorough analysis, and multi-branch work.
Develop new high-performance AI decisions with EXRWebflow and build up digital processes.
Types of AI Agents
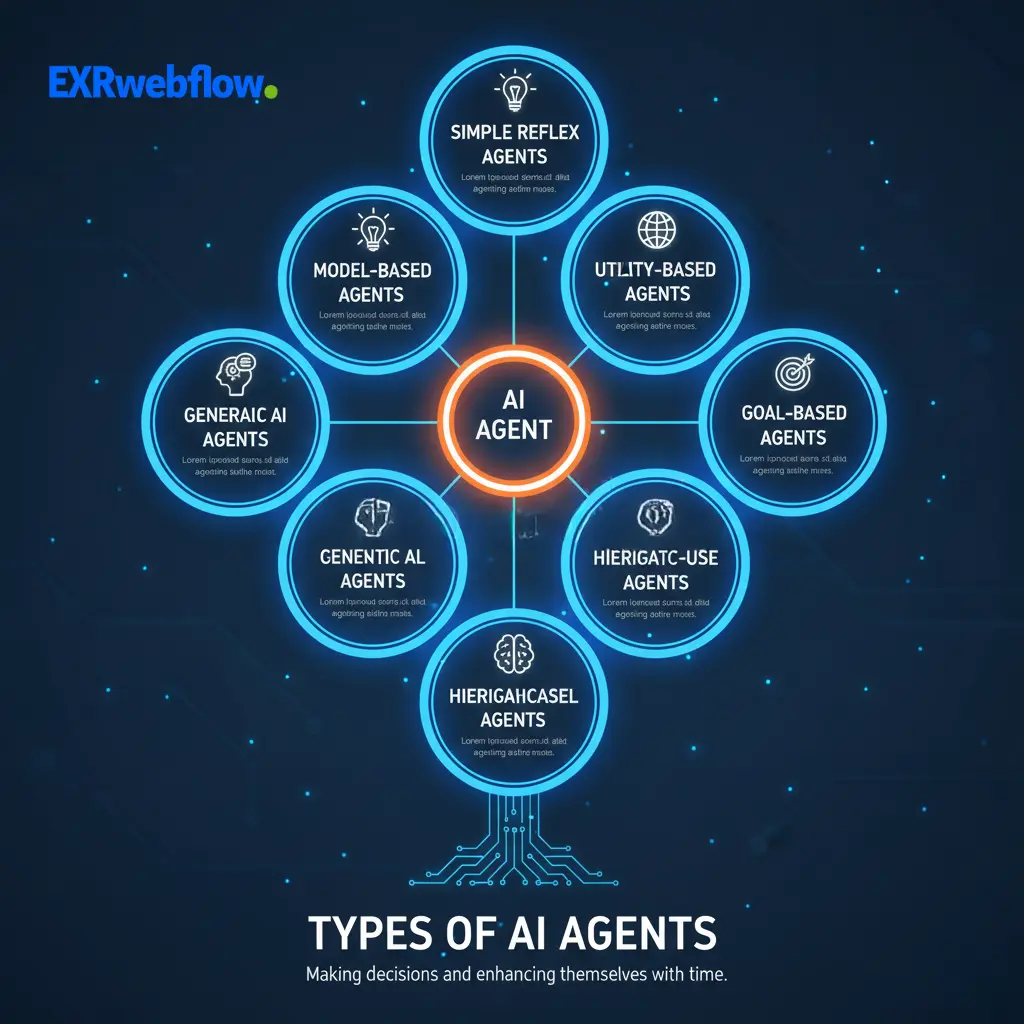
AI agents come in many forms. Each of the types possesses an alternate intelligence, memory, and decision-making capacity.
Simple reflex agents
These agents respond to the prevailing input. They do not use memory. They have simple regulations, like when this occurs, do this.
Model-based reflex agents
Such agents interpret context through memories. They also record the past occurrences to make improved decisions.
Goal-based agents
These agents make decisions depending on the objectives they desire. They strategize and adapt to the steps to be taken towards an outcome.
Utility-based agents
Such agents seek action that they can most benefit from. They put options into consideration and select the most valuable one.
Learning agents
These agents get better through experience. They examine the actions, revise the strategies, and become more effective with time.
Hierarchical agents
These agents work in layers. Top-level agents establish objectives, and the bottom-level agents perform actions. The structure assists in coping with complicated tasks.
General AI agents
Such agents are able to perform many tasks rather than one specialized job. Their reaction involves rash thinking, designing, and the utilization of tools in several fields.
Agentic AI chatbots
These chatbots are able to plan, act, and accomplish. They do not just talk but actually do work using equipment and memory.
Computer-use agents (CUA)
These agents work with software interfaces directly. They use clicks, typing, and navigation systems just like the normal human user would.
Multi-agent systems
Such systems employ a large number of agents. They distribute information, separate tasks, and synchronize efforts to accomplish huge or extensive projects.
What Do AI Agents Do? Use Cases
General Use Cases
Every AI agent is equipped with a system of elements that enable it to comprehend goals, devise actions, and take a significant step.
| Use Case | What the Agent Does | Why It’s Useful |
| Workflow automation | Runs multi-step tasks across apps without human input. | Saves time, removes bottlenecks, and reduces errors. |
| Knowledge and research tasks | Searches, analyzes, and summarizes information. | Speeds up research and improves decision-making. |
| Report generation | Creates reports using data from multiple systems. | Produces accurate documents in minutes instead of hours. |
| Customer support | Handles questions, resolves issues, and updates records. | Delivers fast, consistent support at scale. |
| Sales and lead qualification | Scores leads, sends outreach, and updates CRMs. | Increases conversions and reduces manual follow-ups. |
| Operations automation | Manages scheduling, inventory checks, or system monitoring. | Improves efficiency and prevents routine delays. |
| Software development agents | Writes code, tests features, and helps debug issues. | Speeds up development and reduces repetitive engineering work. |
Industry Examples
The following are industry-specific examples in a simple and straightforward manner.
There is a brief description of each bullet to make it flow and to be understood.
Finance
AI agents result in transactions, identify trends, verify compliance regulations, and create financial reports. They assist teams to mitigate risk and work with real-time visibility.
Manufacturing
Agents keep an eye on the machines, anticipate failures, and schedule production optimally. They assist factories in reducing downtime and increasing efficiency in the running of operations.
Consumer goods and commerce
Agents also modify the prices, monitor the inventory, make customized recommendations, and handle the order workflows. This ensures increased sales and customer experiences.
Automotive
Agents execute diagnostics, verify system behaviours, and simulate support environments. They assist engineers in analyzing performance automatically.
Healthcare
Agents also summarize clinical notes, assist in the triage process, sort records, and perform booking processes. They enable the healthcare teams to pay more attention to patient care.
Service teams
Agents process tickets, monitor customers, and provide recommendations. This will result in quicker resolutions and better service delivery.
Sales and marketing
The agents handle outreach, partition customers, and develop campaigns on a personalized level. They assist test groups to make more conversions and less manual labor.
Software development and IT
Agents code, test, and test deployments and search logs. They assist developers to work faster and eliminating the monotony of work.
Hire an AI developer and begin working on smart automation systems that will work in your favor.
Benefits of AI Agents
The benefits of using AI agents are quantifiable and contribute to increased work speed, smarter, and efficient teams.
- Improved productivity: Agents are used in repetitive and complex work, which leaves teams to work on high-value work.
- Reduced costs: Elimination of labor minimizes labor costs, reduces errors, and wastage.
- Informed decision-making: Agents process real-time data, hence providing intelligence that will assist in making stronger business decisions.
- Customer experience improved: Faster responses, continued contact, and individual interactions are offered to customers.
- Enhanced performance: Agents are accurate, rule-bound, and never lose track, even in a long process.
- Scalability and availability: Agents do not get tired of their work, which ensures that it will be easy to increase the scale of operations at any point.
AI Agents and Business Transformation
AI agents are indeed transforming the way organizations are run. They present another way of working where computer systems are used to run the execution and human directions. This transition alters productivity, costs organizations, and personnel functions.
Impact on business growth
With AI agents, companies become smarter. They minimize the use of hands, and they reduce the time in responding and enabling evidence-based decisions. This enhances faster product delivery, customer service, marketing, and operations. The result is an increased output and fewer points of bottleneck.
Organizational challenges
The uptake of AI agents does not come as naturally. The teams have issues of skill deficiency, process redrawing, personal confidence, and agentic integration into the already established tools. Firms should be ready by training, updating their policies, and rolling out schemes.
AI workforce platforms
Nowadays, AI workforce solutions are used in modern companies. These systems enable teams to generate, release, and control a number of agents. They follow activities, follow-up results, and manage the interactions among agents in the departments.
Changes to tech architecture
AI agents are based on systems that are modular systems. The companies tend to move to API-first software, workflow driven by events, safely controlled data pipelines, and centralized layers of control. This facilitates the agents to deal with tools and keep a standard throughout the activity.
Implementation steps
Business ventures normally begin small. They single out one task whose value is definite. They construct or install an agent to look after that. They observe outcomes, enhance procedures, and add more workflows. As it evolves, they develop a professional AI force that automates whole functions.
Real-World Examples of AI Agents
AI agents are already used in industries. Some of the categories of how they work in practice are shown below.
General-purpose AI agent apps
These agents do general jobs. They handle emails, file management, create summaries, taking analysis of documents, and assist in day-to-day activities in any department.
Enterprise AI workforce platforms
In an enterprise scale, customer support, operations, finance, HR, and engineering agents are deployed. On those platforms, dozens or even hundreds of agents are coordinated.
Developer-focused agents
The engineer deploys a code-writing agent, feature testers, log scanners, and error correctors. These agents make development faster and eliminate repetitive engineering tasks.
Zapier-style agents
These agents are used to automate activities among applications. They activate work processes, integrate data, and perform activities between tools without human intervention.
Case study: enterprise adoption
A typical instance is a support team embracing agents. The agent reads the tickets, finds out the problem, retrieves the history of the customer, recommends fixes, and updates the CRM. The reaction time decreases and the accuracy increases, and the human agents have the capability of specializing in the complex cases.
Best Practices for Deploying AI Agents
Effective deployments of AI agents require order, security, and well-defined policies. To prevent unforeseen behavior, the use of agents as teams is confident that they are used is aided by the following best practices.
- Activity logs: Document all the activities of the agent. This brings in a sense of transparency, facilitates audits, and also makes troubleshooting easy.
- Interruption and kill-switch controls: At any time, agents are to be stoppable. This eliminates loops, safeguards systems, and makes them human-controlled.
- Unique agent identifiers: Assign each agent a unique identifier and authorization. This maintains a well-structured access; it minimizes the threats to security.
- Human supervision: Humans are in charge of the objectives; they monitor achievement and align the achievements of the agent with the business standards.
- Governance and guardrails: Provide a clear limit to what can be done by the agents. Guardrails discourage unwarranted behavior and encourage uniformity.
- Data governance: Regulate the access, storage, and use of data. This safeguards confidential data, and it is also in line with the privacy provisions.
- Workflow integration: Relate agents via APIs, automation levels, and safety tools. With adequate integration, there is precision and less friction.
Risks and Limitations of AI Agents
AI agents are effective, yet they also create difficulties that organizations should be aware of. These dangers do not imply that agents should be refused. All they need is prudent planning, control mechanisms, and human management.
- Multi-agent dependencies: Many agents that are dependent on each other can propagate the error over the chain and lead to bigger failures.
- Infinite feedback loops: Agents can repeat indefinitely in case instructions are ambiguous, or they misunderstand themselves.
- Computational complexity: The high-level thinking and computations need a considerable amount of processing power, which may increase compute costs.
- Data privacy: Sensitive information is frequently accessed by the agents. Unless there is imposition of strict controls, data can be revealed or abused.
- Ethical challenges: Training data may have bias, and the agents will make unfair or inconsistent decisions.
- Technical constraints: Back-end systems, inadequate APIs, or flawed data may prevent the smooth work of agents.
- Accountability issues: In case an agent commits a mistake, it may be unclear who made the mistake without an appropriate level of oversight and recording.
The Future of AI Agents
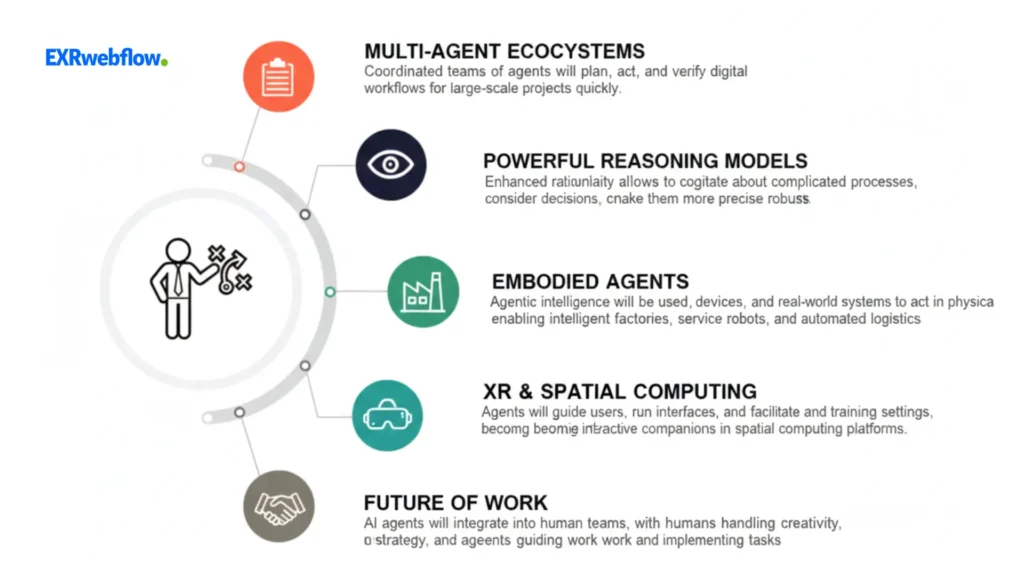
AI agents have moved beyond mere performers of redundant tasks to become complete digital employees. Their development will define the ways that people will utilize software, the ways that companies will work, and teams will engage with smart systems.
Multi-agent ecosystems
There will be a large number of working agents in coordinated teams. Some will plan. Others will act. Others will verify. This forms digital workforces that are able to cope with large-scale projects quickly.
Reasoning models
Rationality models are becoming powerful.
They make the agents cogitate about complicated processes, consider decisions, and make them more precise. Enhanced thinking implies improved agents capable of dealing with challenging workflows.
Embodied agents
The agents will not work on screens anymore. The agentic intelligence will be used by robots, devices, and real-world systems to act in the physical environments. These preconditions enable intelligent factories, robots in the field of services, and automated logistics.
XR and spatial computing integration
The agents will tell the users their direction, run interfaces, and facilitate training in the virtual and augmented setting. They will be interactive companions within a spatial computing platform.
Future of work
AI agents will enter the world of normal teams. They will also implement, as humans are concerned with creativity, oversight, and strategy. There will be a shift in work where tasks will not be done, but guided by intelligent systems that work.
Address your project and find out how AI will change your workflow.
Wrapping Up
AI agents are a significant change in the mechanism of technology. They know what to achieve, set plans, utilize tools, and gain experience. This allows them to be even more competent than chatbots or basic automation. There is now a use of agents to simplify businesses, customer service, accelerate the development, and assist in decision-making.
The use of agents in industries will become imperative as reasoning models and multi-agent systems are enhanced. Those organizations that learn to utilize them will be operating much faster, smarter, and with less efficiently than organizations that are stuck in old workflows.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
What does an AI agent do?
An AI agent perceives a goal, plans activities, operates tools, and executes them with little human assistance.
Is ChatGPT an AI agent?
ChatGPT is not a single agent on its own, but it can be perceived as such when it is tied to memory, tools, and planning modules.
What are examples of AI agents?
These are customer support agents, research agents, sales agents, marketing agents, workflow agents, and developer agents.
What characteristics define AI agents?
The prominent characteristics are autonomy, goal orientation, perception, rationality, proactivity, learning, adaptive, and collaboration.
How do AI agents integrate with workflows?
They interrelate using API, Browsers, software, or automation layers to execute activities within current systems.
What are the pros and cons of AI agents?
Advantages comprise speed, accuracy, lower prices, and increased experiences for customers. Disadvantages involve privacy risks, computing requirements, technical challenges, and dependency concerns.
Are there AI agents for marketing or sales?
Yes. They qualify leads, make outreach, make groups, make personal campaigns, and update CRMs automatically.
What is the difference between an LLM and an AI agent?
An LLM is a reasoning engine. That engine is combined with planning, memory, and tools to be acted on by an AI agent.
What risks do autonomous AI agents pose?
The most notable risks are loops, privacy risks, biased decisions, system failures, and a lack of responsibility.
How does human-in-the-loop fit into agent workflows?
People set objectives, analyze outcomes, and take measures when the necessity arises. This guarantees accuracy, safety, as well as conformity to business rules.


